�@
|
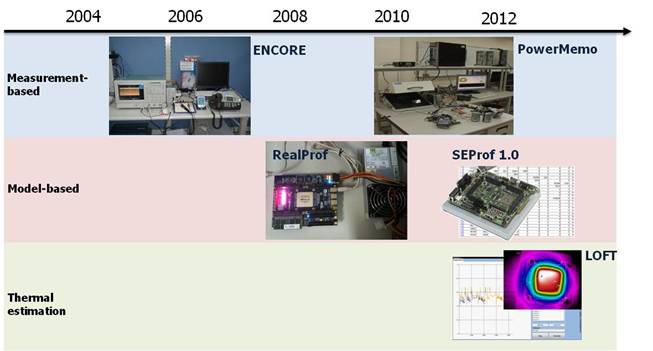
Research Projects Energy Profiling and Monitoring
Tools for Embedded Software: A number of tools were
developed for evaluating thermal behaviors and energy consumption of embedded
software. Those tools are: ENCORE: energy conserving wireless LAN phone, PowerMemo: power meter for mobile devices, RealProf: hardware-assisted energy consumption evaluation
tool, SEProf: high-Level software energy profiling tool, and LOFT: fast
thermal estimation for microprocessors.
BuildingSense: A number of studies have proposed information and
communication technologies for improving energy efficiency of a smart and
green building. However, it is still a challenging issue to detect the energy
inefficiency of indoor activities in a space and/or building, and to infer
possible reasons for the energy inefficiency. In this study, we investigate
new energy and activity sensing technologies to identify indoor activities
and gather the meta-data of activities such as type, location, number of
participants, appliances in used and their states.
SEEDS: A Solar-Based
Energy-Efficient Distributed Server Farm: Distributed
and renewable energy has emerged as a promising resource because of its
environmental friendliness and economic considerations. However, most
renewable energy sources are unreliable and may require considerable effort
to be efficiently utilized in a computing center for providing services and
supporting applications. In this paper, we exploit distributed renewable
energy (e.g., solar energy) and peer-to-peer (P2P) technologies to aggregate
distributed computing power to provide an infrastructure called Solar-based
Energy-Efficient Distributed Server (SEEDS) farm for distributed computing
and distributed storage.
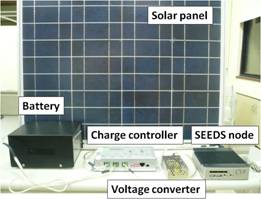
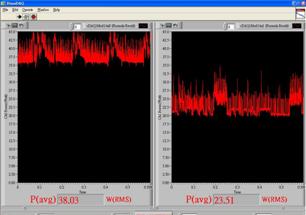
Prototype of SEEDS. (a) Solar power
supply system. (b) Prototype implementation. (c) Screenshot of power
measurement program (the conventional server is on the left side and the
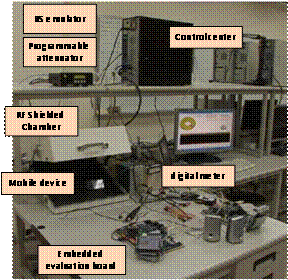
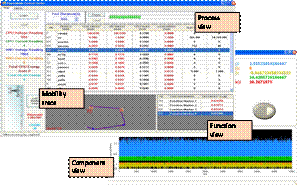
SEEDS server is on the right side). PowerMemo: An Energy Consumption Profiling Tool for Mobile
Applications in an Emulated Wireless Environment: We
present architecture and implementation of a measurement-based energy
profiling tool with software controllable wireless environment for mobile
devices, called PowerMemo (power meter for mobile).
The tool composes of a software event profiler and power measurement hardware
to analyze the process-level and function-level power consumption of mobile
applications on a Java and Android/Dalvik virtual
machine. The control of signal attenuators and RF-shielded chambers are integrated to the tool so that
developers can emulate a real-life mobility scenario that a mobile device may
encounter. The proposed tool overcomes the issue of power consumption
profiling of asynchronous I/Os and can correlate energy consumption of I/O
events with high-level software activities. This tool gives developers a
broader view of energy consumption and network behavior in mobile software so
that the developers can optimize the energy efficiency of their mobile
applications.
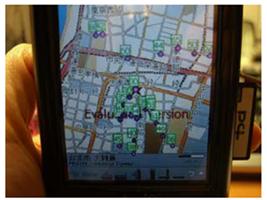
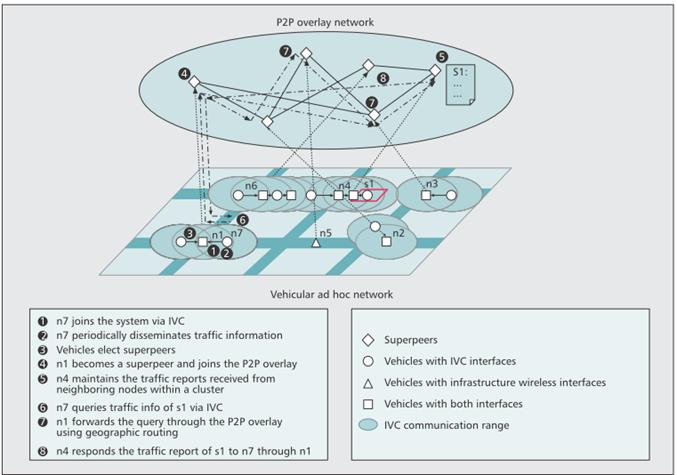
PowerMemo Demo P2PNavi: A Two-Tier Peer-to-Peer Traffic
Information System: Decentralized traffic
information systems realize real-time traffic information services without the
need for a server infrastructure. However, existing systems rely on either
the vehicular ad-hoc network or application-layer peer-to-peer protocols over
a broadband wireless network suffering from low lookup success rate, high
lookup latency, and maintenance overhead of the P2P network. This study proposes a
two-tier VANET/P2P architecture that exploits both VANET and P2P
technology. In the low tier, vehicles form a VANET via inter-vehicle communication
to exchange traffic information. On top of the VANET, a portion of the
vehicles further establish a P2P overlay through a broadband wireless
infrastructure to mitigate the disconnectivity
problems of the VANET.
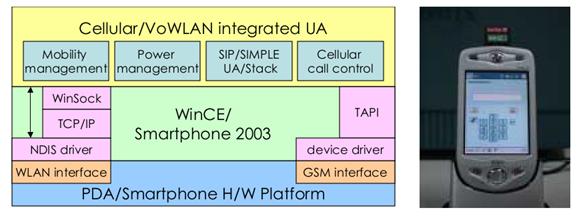
PIANO: a low power cellular/VoWLAN
dual-mode mobile: The integration of cellular
and VoIP over WLAN (VoWLAN) systems recently has
attracted considerable interest from both academia and industry. A cellular/VoWLAN dual-mode system enables users to access a
low-cost VoIP service in a WLAN hotspot and switch to a wide-area cellular
system without WLANs. Unfortunately, cellular/VoWLAN
dual-mode mobiles suffer the power consumption problem that becomes one of
the major concerns for commercial deployment of the dual-mode service. In
this study, we present a novel power saving mechanism, called PIANO (paging
via another radio), for the integration of heterogeneous wireless networks,
and further apply the proposed methods to implement a cellular/VoWLAN dual-mode system.
Prototype of PIANO on Mobile Devices �@ |
||||